iVABS Enables VABS for Design and Optimization, Parametric Studies, Uncertainty Quantifications & More
iVABS is an integrated framework developed by Purdue University with support from the US Army that can be used with the desktop version of VABS. iVABS enables VABS for design and optimization, parametric studies, uncertainty quantifications, etc. iVABS also makes it possible to link the powerful capabilities of VABS to third-party structural solvers such as RCAS, CAMRAD II, Dymore, and others. The release packages for either Windows or Linux and the complete documentation can be found at the iVABS website.
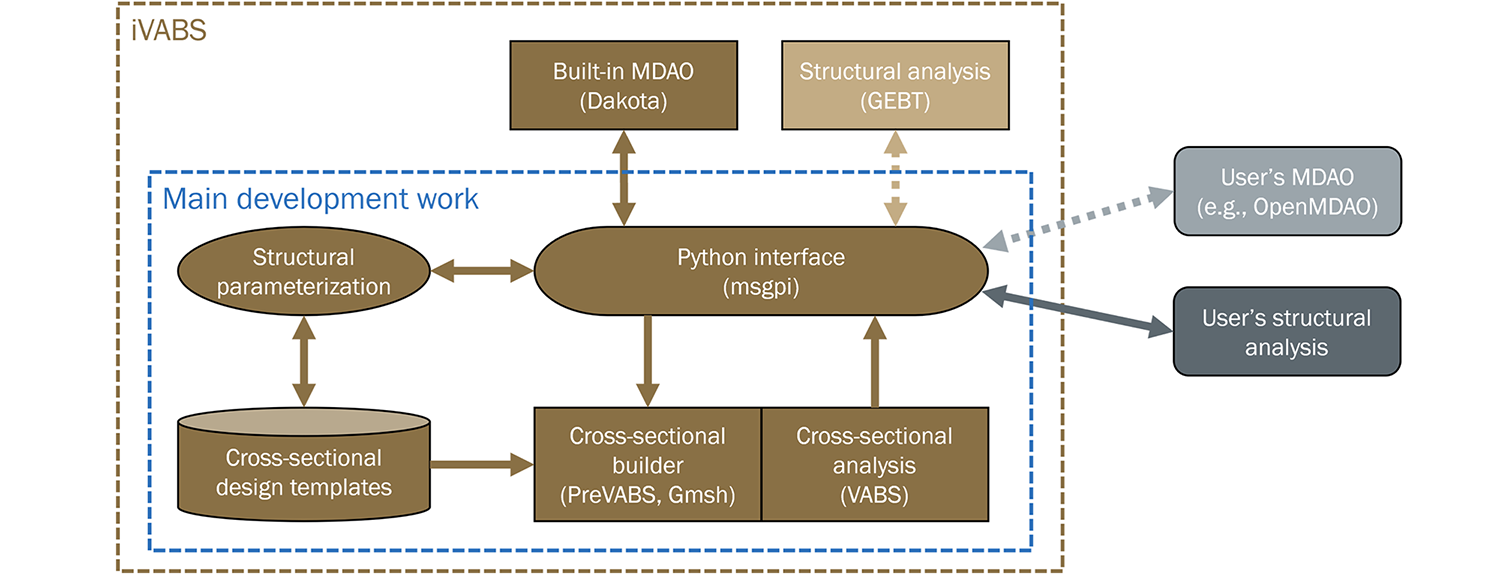
Short for integrated VABS, iVABS is a design framework for composite slender structures (also called composite beams) such as helicopter rotor blades, air mobility blades (AAM, UAM, eVTOL), wind turbine blades, high aspect ratio wings, golf clubs, bridges, poles, columns, rods, tubes, shafts, etc. This framework bundles PreVABS, VABS, GEBT, Dakota, along with MSGPI for integration among these codes and other codes. PreVABS, VABS, GEBT, and MSGPI are developed by Prof. Wenbin Yu’s research group. Dakota is developed by the Sandia National Lab. The relations of different components are described in the following figure. A brief introduction of different components can be found in the iVABS Components page. VABS works with the desktop version of VABS, which is available from AnalySwift.
VABS is a uniquely powerful approach to modeling composite blades and other slender structures (beams). VABS reduces analysis time from hours to seconds by quickly and easily achieving the accuracy of detailed 3D FEA with the efficiency of simple engineering models. With continuous development spanning over 20 years for performance and robustness, VABS is used in the aerospace and wind energy industries for modeling complex composite rotor blades, wing section design, and simulating other slender structures. VABS can accurately compute the complete set of beam sectional properties for slender structures featuring arbitrary cross-sectional shape and materials. It can reproduce the accuracy of direct numerical simulation using 3D FEA by explicitly modeling all the ply details of composite beams. In addition to PreVABS, VABS directly interfaces with ANSYS, ABAQUS, and others.